-
Introduction
Two patent applications have been submitted addressing issues associated with
measuring friction in a pair of axially loaded bearings and in a pair of radially
loaded bearings, in both cases using a standard, axially loaded, rotary tribometer.Radially Loaded Bearing Friction Adapter
Patent Application: GB2504361.3
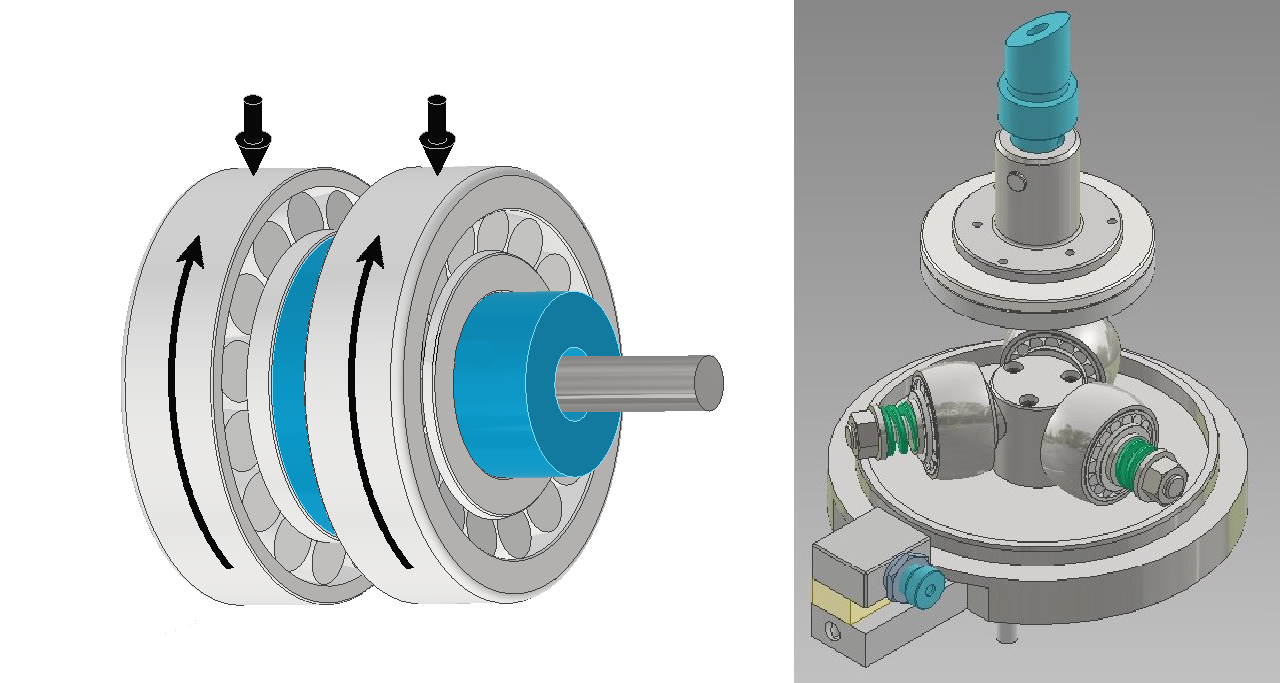
In this device, three pairs of bearings are mounted in separate housings and fitted
onto three shafts, projecting radially from a common hub, much in the same way
as taper roller bearings are mounted as wheel bearings on axles.
A rotating disc, mounted on the tribometer spindle, is then used to apply a radial
load to the bearing pairs and to impart rotation. Friction in the bearings is reacted
by torque in a horizontal plane, through the centre line of the axles. This results
in torque on the adapter hub, which is then sensed by torque reaction mounting
the adapter in the conventional way.
Hence, friction torque generated by six radially loaded bearings can be measured
using as standard axially loaded rotary tribometer.Axially Loaded Bearing Friction Adapter
Patent Application: GB2501479.6
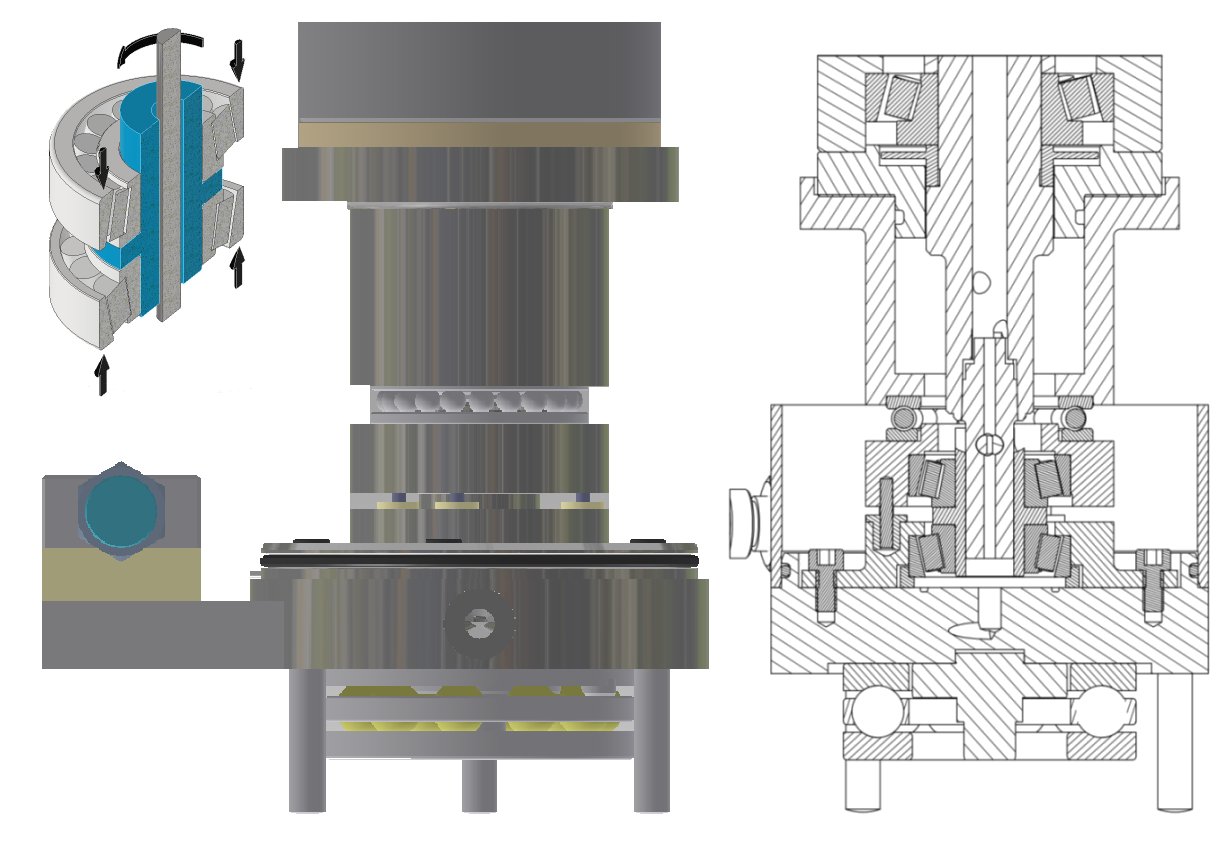
There are usually limitations to the maximum axial load that can be applied to a
test bearing in a conventional axially loaded rotary tribometer. This is because
the axial load is normally reacted by the tribometer spindle bearings, which will
be of finite capacity. To overcome this limitation, identical bearings can be
mounted back-to-back, with higher axial loads reacted, not by the spindle
bearings, but by the spindle housing itself.
If instead of a solid connection between the upper test bearing carrier and the
spindle housing, a ball thrust bearing is included in the force path, friction torque
generated in the upper bearing would cause it to rotate. Sliding pins between the
upper and lower bearing carriers will transmit this friction torque to the lower
bearing.
Hence, with the lower bearing assembly torque reaction mounted in the
conventional way, the sum of the friction torques generated by the two identically
loaded test bearings can be measured, at axial loads that far exceed the nominal
capacity of the rotary tribometer spindle bearings. -
Download the Machine Leaflet

